{{t.docname}}
{{t.testdescription |htmlToPlaintext}}
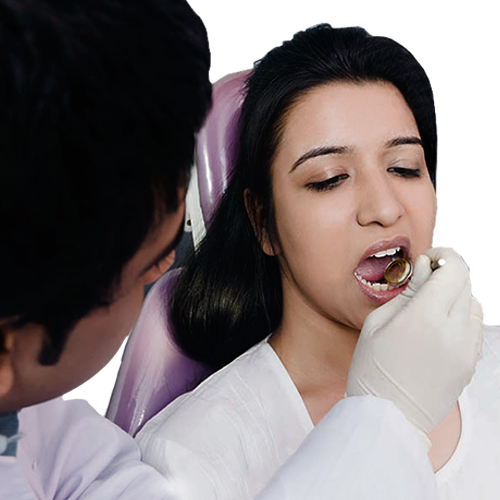
Emergency Dental Centre (EDC) – your choice for immediate pain relief. We understand that oral discomfort is not just a slight inconvenience – oftentimes, it’s a painful dental issue that needs addressing as soon as possible. At EDC, we know that many of our patients’ dentistry needs are complex, which is why we are proud to offer family, restorative and cosmetic dentistry all under one roof.
Building a foundation of trust by treating patients as special individuals. We at EDC understand how uneasy some patients may feel about their dental visits, and how we can make a difference in providing a relaxing and positive experience via EDC Centres. We are dedicated to providing excellent, personalized care and service to make visits as comfortable and pleasant as possible.
We are commitment to provision of optimal oral health. We provide not just the emergency treatment using the most advanced, state-of-the-art techniques and equipment to relieve pain but also educate the patients to make more informed decisions about their oral health needs.
Our forte is that EDC Centres or dental clinics are operated by dental professional dedicated to optimal dental health by providing high quality personalized dental care designed both for preventative care and education to ensure that you enjoy optimal dental health.
Experience all that modern dentistry has to offer at EDC Centres. Our goal is to assist each patient in achieving and maintaining long term oral health and a beautiful smile.
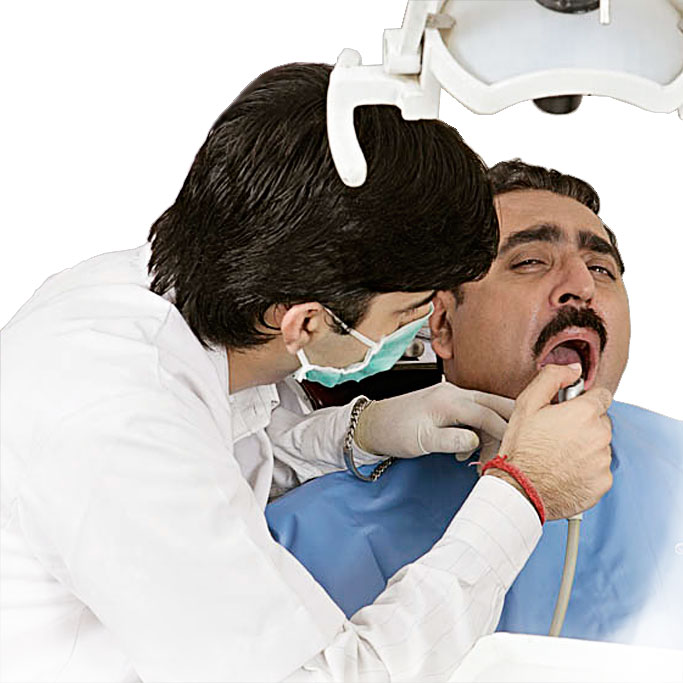

Emergency Dental Clinic (EDC) are a network of dental clinics that provide service for individuals who need emergency dental services or late night dental services on any day of the week. Whether you have a toothache or broken crown or dental infection we are the primary source for immediate dental care. Let us help relieve your dental pain give us a call by finding the nearest EDC Centre to you.

You are welcome to this forum to meet, share, learn, and discuss various dental topics and issues related to dental emergencies. Join the conversation to contribute, discuss, and interact with others and our dental team to enjoy optimal dental health.
Did you know that calcium and phosphorous found in cheese is healthy for your teeth – it reduces the pH level in plaque and re-mineralizes the enamel
Did you know that a sore jaw, when combined with chest pain, can signal a heart attack- especially in women.
Did you know that dental pain can range from minor gum irritations to severe tooth infections. As a general rule, pain needs to be addressed quickly if it happens spontaneously, keeps your child awake at night, or doesn’t respond to pain relievers.
Did you know that saliva prevents tooth decay. Saliva contains components that can directly attack bacteria which cause decay, and it is also rich in calcium and phosphates that help to remineralise tooth enamel. Saliva contains antimicrobial components, as well as minerals that can help rebuild tooth enamel after attack by acid-producing, decay-causing bacteria.
Did you know that if you cut or bite tongue, Lip or Cheek to apply cold compresses to injured areas to help control swelling and bleeding. If bleeding cannot be controlled by simple pressure, rush to a hospital emergency room.
Did you know that if you Knock-Out a permanent tooth you should handle the tooth by the crown, not by the root. Rinse the tooth with water to remove dirt. Inspect the tooth for fractures. If it appears whole, try to reinsert it into the socket. The tooth should displace the blood clot relatively easy. If excessive force is needed, do not continue to reinsert the tooth. Rush to the dentist.
Did you know that if a primary (baby) tooth is knocked out then do not try to reinsert the tooth. You may apply cold compresses to injured areas to help control swelling and bleeding. Baby teeth are not reinserted because of the potential for damage to developing permanent tooth buds. Usually this type of injury does not need immediate follow-up.
Did you know that in case of Chipped or Fractured permanent Tooth rinse the mouth with water and apply cold compresses to reduce swelling. Locate any broken tooth fragments, place them in milk, and bring them with you to the dentist.
Did you know that Chipped or Fractured primary (Baby) Tooth usually does not require immediate attention if the fracture only involves the outer shell of the tooth. If a larger part of the tooth is fractured you should contact your dentist. Small fractures of primary teeth are very common. This is particularly true when children are learning to walk.
Did you know that in case of severe Blow to the Head rush to the nearest hospital emergency room immediately, especially in cases of loss of consciousness or experiences vomiting.
Did you know that in case of possible Broken or Fractured Jaw keep the jaw from moving and rush to the nearest hospital.
Did you know that people with Gum disease are at higher risk for developing heart disease, stroke, uncontrolled diabetes, pre-term births and respiratory disease.
Did you know that periodontal bacteria can enter the blood stream and travel to major organs and begin new infections.
The most effective intervention is prevention. We are in a unique position to help families prevent accidental trauma, including oral trauma, by providing anticipatory guidance here at our web site.
Tooth injury can be divided into the following classifications, ranging from mild to severe injury:
Injury to the tooth and its supporting structures without causing abnormal loosening or displacement of the tooth. Tooth is tender to percussion.
Advise: Stick to a soft diet for 2 weeks. Monitor for changes in tooth color. There may be possible injury to developing permanent teeth from trauma if a primary tooth is injured.
Preventive caresafety gates and furniture protectors are very important and mouth guards while playing sports.
Injury to the tooth and its supporting structures with abnormal loosening but no displacement. Tooth is tender to percussion, with bleeding at gingival margin.
Advise:Rinse with cold water. Stick to a soft diet for 2 weeks. Monitor for changes in tooth color that may indicate pulp necrosis.See the dentist immediately.
Lateral Luxation Injury to the tooth and its supporting structures, resulting in tooth displacement. Injured tooth is at risk for pulpal necrosis and root resorption.
Advise: Rinse with cold water. Keep an ice pack over the lip and mouth if swelling is present. Stick to a soft diet for 2 to 4 weeks, depending on type of injury. See the dentist immediately.
Intrusion Tooth is pushed into the socket and the alveolar bone. May appear shortened or barely visible. Offers poor prognosis and high risk for complications, including root resorption, pulp necrosis, and infection. May require a root canal.
Advise: This type of injury may damage underlying permanent teeth, especially if an infection develops. Teeth may re-erupt in 2 to 6 months. If a primary tooth does not re-erupt, it will require extraction to not interfere with permanent tooth eruption.
Extrusion Tooth is partially displaced from its socket. This type of injury will require repositioning and stabilization. Immediate dental visit is needed.
Avulsion Tooth is completely out of the socket. Management will depend on tooth type.
Uncomplicated fracture of the enamel Fracture (crack) of the enamel without involving the dentin or the pulp. May have a sharp edge.
This type of fracture is rarely painful
Uncomplicated fracture of the enamel and dentin An enamel-dentin fracture that does not involve the pulp and can be recognized by the yellow to pink color of the dentin. Potential complications include pulp death or infection.
Advise: The child can rinse the oral cavity with warm water. Provide a soft diet, avoiding temperature extreme.
Uncomplicated crown fracture An enamel-dentin fracture with pulp exposure. The fracture site has a reddish tinge or will show some bleeding. This type of fracture can cause extreme pain and may lead to pulpal necrosis. It also presents a risk of root resorption and infection in exposed pulp.
Advise: The child can rinse the oral cavity with warm water. If facial swelling is present, use cold cloth or ice pack to reduce swelling.
Root fractureA fracture with pulp exposure. Potential complications for a root fracture include root resorption and pulp necrosis.
Advise:Refer to dentist as soon as possible (within 12–24 hours) fr evaluation, where diagnosis is made radiographically. Excessive mobility of the tooth should lead to suspicion of root fracture. Treatment consists of reduction and splinting for permanent teeth, or extraction, depending on the extent of the traumatic lesion.
Injury to the Lip Swelling and bruising of the lips are common after oral trauma, even in the absence of laceration.
Injury to the frenum The frenum is likely to be torn as a result of a fall that causes trauma to the mouth or teeth. A torn frenum heals spontaneously without long-term consequences.
Advise: Avoid citrus or acidic foods.
The dental visit is essential in order to establish a complete and correct diagnosis of all soft and hard tissue injuries. For this the dentist will follow the below mentioned procedure:-
With advanced skills, techniques and technologies we can save injured teeth. Find an emergency dental Centre right away!

Effort can be made to reduce the prevalence of traumatic injuries by taking into consideration the following measures:

Indian Dental Association (IDA) is the national voice for dentistry, aims “to promote the science and art of dentistry and the betterment of public oral health” through effective communication, guidance and thoughtful legislative efforts. We are dedicated to serving the interests of our members and promoting oral health.